RootViz FS, a plant root X-ray scanning imaging analysis system from Phenotype Screening, USA, is a new, efficient, high-precision, non-destructive measurement system used to perform in-situ imaging analysis of the roots of potted plants, allowing the root system to be photographed.Stereo X-ray photo. This system is an exciting invention in the field of plant root system research after the rhizotron system (such as the Canadian Regent WinRHIZO root system analysis system).After the root detection system needs to be removed and cleaned, it is analyzed with the help of a scanner. This process often breaks the fragile parts of the plant's root tip, and it is an ex vivo analysis and cannot be dynamically monitored.Plant root X-ray scanning imaging analysisThe system is a non-destructive in-situ analysis system that can analyze all parts of the plant root system (including root apices, etc.) in an all-round way, and long-term dynamic monitoring of root system growth can be carried out at different stages of plant growth.This system is very suitable for studying the dynamic response of plant roots to stress, and can analyze plants with a plant height of 2.0m and a root depth of 1.0m. | ||
 |  |  |
Main control computer | Host System | System internal structure |
Main functions | |||
ØIn situ, non-destructive study of plant roots ØA comprehensive analysis of all parts of the plant root system ØLong-term monitoring of plant root growth dynamics ØGet root system information with large capacity, high efficiency and high precision ØRapid screening of root mutant strains in large batches ØPhysiological and pathological research on root systems under fully controlled conditions ØNon-destructive detection of plant stems ØNon-destructive detection of plant seeds | |||
Application areas | |||
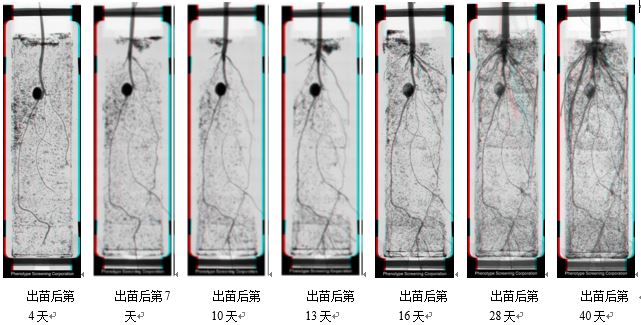
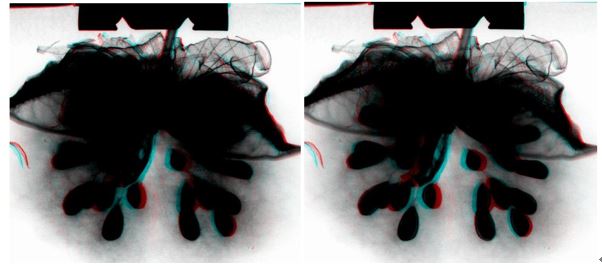
Application Example 1: Dynamic monitoring of root growth and development | |||
| |||
Monitoring of dynamic growth of roots 40 days after corn emergence | |||
usered/blueThree-dimensional glasses can watch three-dimensional effects | |||
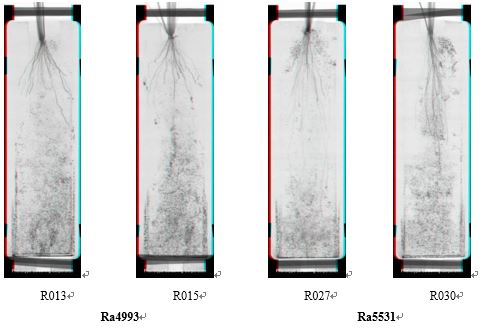
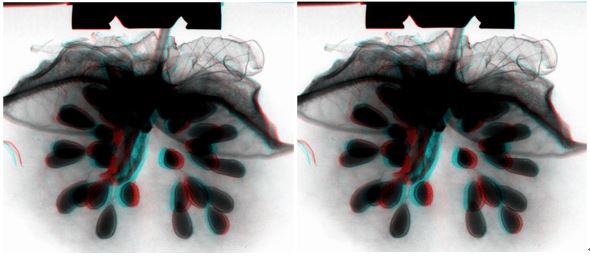
Application Example 2: Differences in root systems between different varieties | |||
| |||
A relatively large angle distribution, Relatively shorter, thicker roots | A relatively small angle distribution, Relatively long and thinner roots | ||
The differences in root systems between different variants of the two rice (Ra4993 and Ra5531) can be easily analyzed using the X-ray scanning imaging system of the plant root system, while the traditional method of post-root scanning will ignore the differences in angles between root systems. | |||
usered/blueThree-dimensional glasses can watch three-dimensional effects | |||
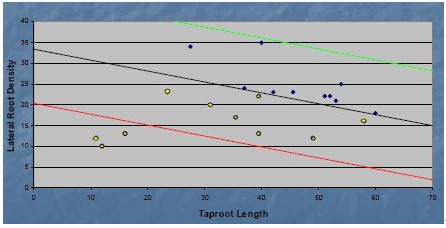
Application Example 3: Root System Classification | |||
| |||
It is difficult to distinguish different plant root systems with the naked eye.With the results of the X-ray scanning imaging analysis system of plant roots, the scatter plots obtained by lateral root density and main root length as the coordinate axes can be classified.In the figure above, multiple variants are distributed in the upper part of the center line, while normal varieties are distributed in the lower part of the center line.After the two varieties are hybridized, this method can be used to quickly scan multiple characteristics of offspring. | |||
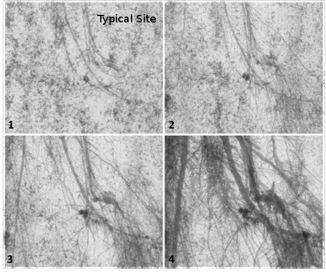
Application Example 4: Root system response to stress | |||
The special culture medium does not contain nutrients, moisture and any pests, so researchers can easily add different nutrients, moisture and pests to conduct stress response research. | |||
| |||
Count measurements of nodule nematodes, the above figure is a demonstration trend of nodule changes over time | |||
Application Example 5: X-ray imaging study of plant stems | |||
| |||
Low-energy X-ray imaging technology can detect the ear stems of corn non-destructively. The above picture is the actual picture of the ear stems of corn ears that are obtained. | |||
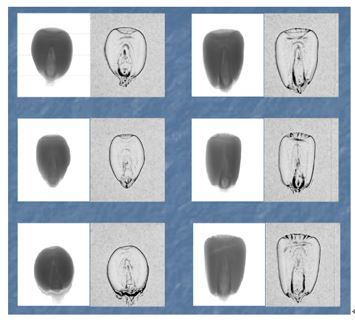
Application Example 6: Research on Seed X-ray Imaging | |||
| |||
Non-destructive study of the internal structure of plant seeds, and compare the differences between different individuals of the same species. The above picture is a corn seed imaging picture | |||
Application Example 7: Research on X-ray imaging of cotton wool | |||
| |||
| |||
Viewing the three-dimensional structure of the inner sleek through three-dimensional glasses can analyze the detailed information of different parts of the inner sleek. The above picture is a three-dimensional picture of the inner sleek. | |||
Main technical parameters | |||
1.1Working conditions: ØAmbient temperature: -5~+45℃ ØRelative humidity: 0-80% ØSuitable power supply: 220-240 VAC 1.2Technical specifications and requirements: 1.2.1technologySpecification 1 Nosystem: ØHost: 1.870 (height) x 0.915 (length) x 0.610 (width) m ØX-ray emitter (50 kVp, tungsten target, spot diameter ~35μm, working intensity 25kVp, 0.3mA) ØDigital X-ray Camera (2940 Small 2304Pixels) ØPlant sample positioning system (adjustable in vertical direction 1m, adjustable in horizontal direction 38cm, and can rotate 360 degrees) ØX-ray protection device (internal lock and indicator light, Chinese/English label) ØMain control computer: Win7 64-bit English system, 1000 G data storage, X-ray system control and image acquisition system ØGraphics and Image Analysis Computer: Linux Mint 64-bit operating system, 32G memory, image processing system ØSpeed: Plan view ≥20 plants/h; Stereo view ≥15 plants/h ØMeasurement range: maximum root length ≤1.0 m; maximum plant height ≤2.0 m Ø"R" type fixing frame, 45x200x1000 mm culture pot and corresponding culture medium Ø"Q" type fixing frame, 45x200x500 mm culture pot and corresponding culture medium 0.5 Nosystem: ØHost: 1.829 (height) x 0.915 (length) x 0.610 (width) m ØX-ray emitter (50 kVp, tungsten target, spot diameter ~35μm, working intensity 25kVp, 0.3mA) ØDigital X-ray Camera (2940 Small 2304Pixels) ØPlant sample positioning system (adjustable 0.5m in vertical direction, adjustable 38cm in horizontal direction, and rotate 360 degrees) ØX-ray protection device (internal lock and indicator light, Chinese/English label) ØMain control computer: Win7 64-bit English system, 1000 G data storage, X-ray system control and image acquisition system ØGraphics and Image Analysis Computer: Linux Mint 64-bit operating system, 32G memory, image processing system ØSpeed: Plan view ≥20 plants/h; Stereo view ≥15 plants/h ØMeasurement range: maximum root length ≤0.5 m; maximum plant height ≤2.0 m Ø"Q" type fixing frame 45x200x500 mm culture pot and corresponding culture medium 1.3Parameters available 1.3.1 Use ImageJ to help process images to obtainPlant root length, root angle and root system spatial distribution map(Relative to the central axis). 1.3.2R Hi traitsRoot system analysis software (optional) ØTotal root length, total projection area and total volume; ØYou can obtain more than 5 different levels of root distribution pictures, as well as the root length and projection area of root systems of different levels of root systems; ØThe location of root systems distributed at different depths; ØThe diameter of root systems at different depths; ØDensity of root systems distributed at different depths. | |||
Origin: Phenotype Screening Company, United States | |||